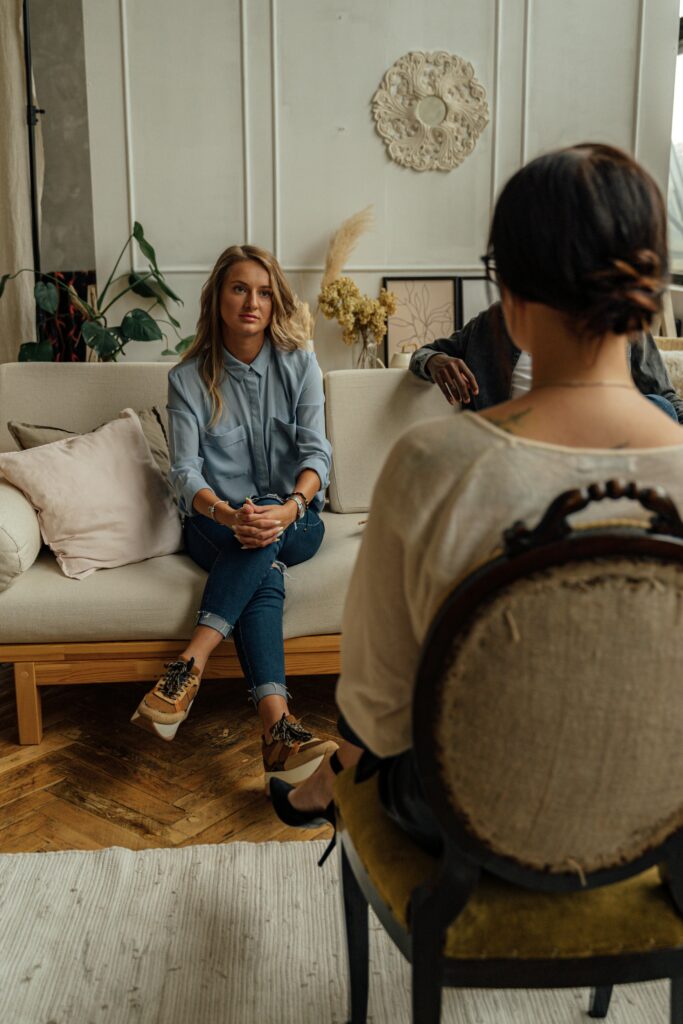
The Importance of Compassion in Trauma Therapy

The Importance of Compassion in Trauma Therapy
Trauma therapy is a specialised field aimed at helping individuals recover from the psychological and emotional wounds caused by traumatic experiences. Whether the trauma stems from abuse, accidents, natural disasters, or other distressing events, the healing process can be complex and deeply challenging. One of the most critical elements in effective trauma therapy is compassion from the therapist and self-compassion from the client.
Understanding Compassion in Trauma Therapy
Compassion involves recognising someone’s suffering and a genuine desire to alleviate it. In trauma therapy, compassion creates a safe and supportive environment where clients feel understood and accepted without judgment. This compassionate approach is essential because trauma often leaves individuals feeling isolated, ashamed, or fearful of being misunderstood.
Why Compassion Matters
- Builds Trust and Safety
Trauma survivors often struggle with trust due to the nature of their experiences. A compassionate therapist can help rebuild this trust by demonstrating empathy, patience, and genuine care. This sense of safety encourages clients to open up, which is crucial for effective healing. - Reduces Shame and Self-Blame
Many trauma survivors carry heavy burdens of shame and self-blame. Compassion helps counter these feelings by fostering a non-judgmental space where clients can explore their experiences and emotions without fear of criticism. - Enhances Emotional Regulation
Compassionate therapy can help clients learn to soothe themselves and manage overwhelming emotions. This is particularly important because trauma often disrupts emotional regulation, leading to anxiety, depression, or flashbacks. - Encourages Healing and Growth
When compassion is present, clients are more likely to engage actively in therapy and develop resilience. It empowers them to view their trauma as a part of their story—not the whole story—and to cultivate hope for recovery and growth.
Self-Compassion: A Key Component
In addition to receiving compassion from their therapist, clients benefit significantly from developing self-compassion. This means treating oneself with kindness, understanding, and patience in the face of suffering. Self-compassion can reduce feelings of isolation and increase motivation for healing.
Implementing Compassion in Trauma Therapy
Therapists can cultivate compassion through active listening, validating feelings, and maintaining a calm, accepting presence. Techniques such as mindfulness, loving-kindness meditation, and narrative therapy often incorporate compassionate elements to support clients’ healing journeys.
Conclusion
Compassion is not just a soft skill in trauma therapy but a fundamental necessity. It lays the foundation for trust, emotional safety, and effective healing. By prioritising compassion, therapists can help trauma survivors reclaim their lives and move toward a future marked by resilience and hope.
Leave a Reply