
Evidence-Based Treatments for Trauma Recovery
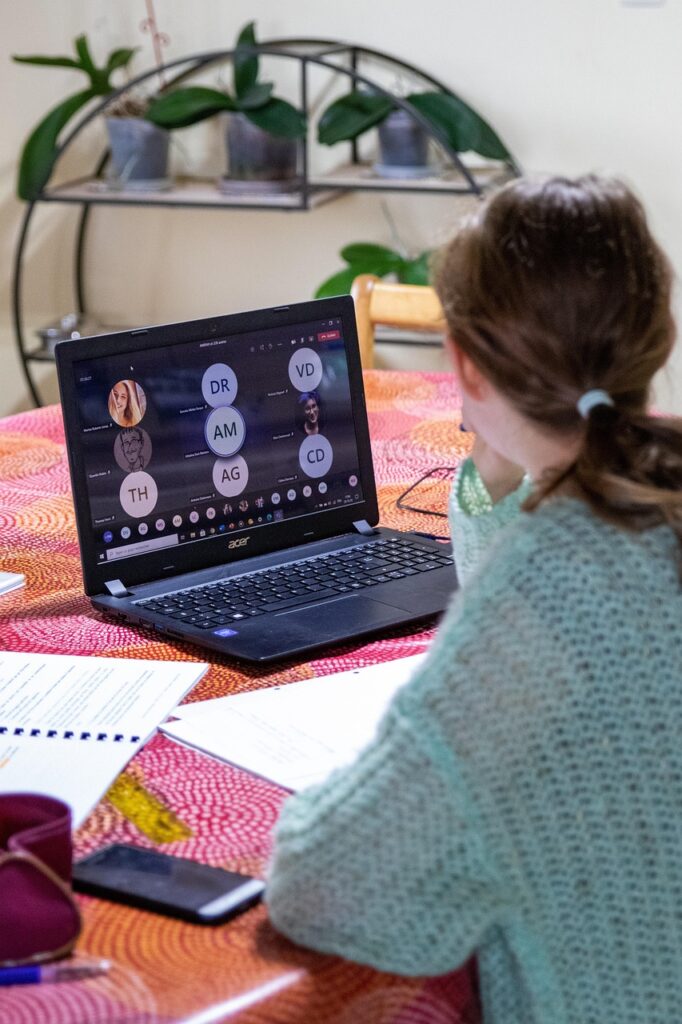
Trauma can have profound and lasting effects on an individual’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Recovery from trauma often requires professional intervention, and evidence-based treatments are effective in helping individuals heal and regain control over their lives. These treatments are supported by rigorous scientific research and clinical trials, ensuring their efficacy and safety. Below are some of the skills-based, evidence-based therapies for trauma recovery:
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a widely used therapeutic approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviours associated with trauma. Trauma-focused CBT (TF-CBT) is a specific form designed for trauma survivors, especially children and adolescents. This therapy helps patients process traumatic memories, reduce distressing symptoms, and develop coping strategies. - Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR is a structured therapy that encourages the patient to briefly focus on trauma memories while simultaneously experiencing bilateral stimulation (usually eye movements). This process is believed to help the brain reprocess traumatic information, reducing its emotional impact. EMDR is effective for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other trauma-related conditions. - Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE)
Prolonged Exposure Therapy involves helping patients confront trauma-related memories, feelings, and situations in a safe and controlled environment. Through repeated exposure, the fear and avoidance associated with trauma gradually diminish. PE is one of the most empirically supported treatments for PTSD. - Trauma-Informed Care
While not a specific therapy, trauma-informed care is an approach that recognises the wide range of trauma and integrates this understanding into all aspects of service delivery. It emphasises safety, flexibility, choice, collaboration, and empowerment, ensuring that care environments do not inadvertently re-traumatise individuals. - Pharmacotherapy
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms related to trauma, such as anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly used and have FDA approval for PTSD. Medication is often used in conjunction with psychotherapy for optimal outcomes. - Narrative Exposure Therapy (NET)
NET is a short-term therapeutic approach that helps individuals construct a coherent narrative of their traumatic experiences. This process aids in contextualising traumatic memories, reducing symptoms of PTSD.
Conclusion
Recovery from trauma is a highly individual process, and what works for one person may not work for another. However, evidence-based treatments provide a solid foundation for effective trauma recovery interventions. If you or someone you know is struggling with the aftermath of trauma, seeking help from a qualified mental health professional trained in these evidence-based approaches can be a crucial step toward healing and reclaiming a fulfilling life.
Leave a Reply